Shoulder pain can be very unpleasant: it often restricts the patient's mobility and affects the quality of sleep. It impairs the overall quality of life - which is why those affected suffer considerably.
30% of the Swiss population are affected by shoulder pain, reports the Rheumaliga in a national campaign. The pain is often caused by sports injuries or occupational activities involving arm movements above head height. Joint wear and tear or muscle tension are also among the most common causes.
Are you also affected by shoulder pain and would like to find out more about possible causes and treatment methods? If so, this article is for you.
The anatomy of the shoulder joint
Before we look at the causes and treatment methods, we would like to briefly discuss the anatomy of the shoulder joint. The shoulder is the most mobile and complex joint in the human body. It allows us to move our arms in almost all directions. However, this mobility comes at a price: the shoulder joint is extremely susceptible to injury. Unfortunately, the underlying causes are not always easy to identify due to the complexity of the joint.
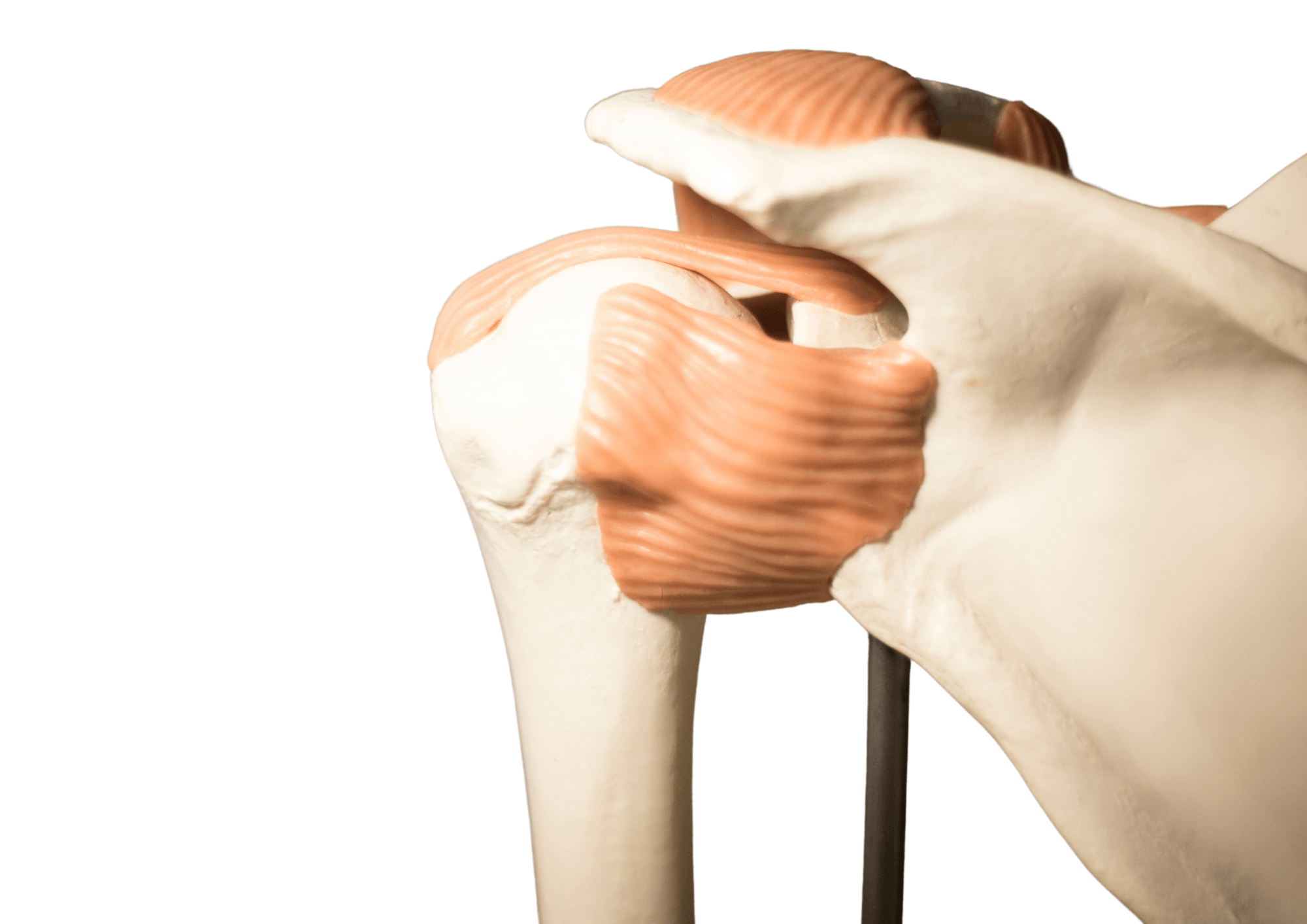
The shoulder joint connects the upper arm bone to the shoulder blade and is made up of two joints: In the first joint, the round humeral head connects flexibly with the glenoid cavity. In addition, the acromioclavicular joint, which is located between the collarbone and the acromion, ensures the vertical mobility of the shoulder joint. The two shoulder joints are muscularly connected to the torso and arms via the so-called shoulder girdle.
Possible causes of shoulder pain
Due to the complex anatomy of the shoulder, pain in this area can have many different causes. The most common include tension or overexertion of the shoulder muscles, bone and joint diseases, injuries to the ligaments and, very rarely, tumors. Metabolic problems such as thyroid disease or diabetes can also contribute to pain in the shoulders.
The shoulders are also relatively susceptible to sports injuries. These occur when unpredictable movements are performed, the body is inadequately prepared for the activity being performed or the range of motion is exceeded. On the other hand, a lack of movement in everyday life can also be responsible for shoulder problems. Poor posture can aggravate pain in the back and shoulders.
Below we describe the most common musculoskeletal disorders or injuries that can lead to shoulder pain:
Impingement syndrome
Shoulder impingement (also known as tight shoulder syndrome) occurs when soft tissues such as tendons or bursae become trapped in the shoulder during movement, which can lead to pain and irritation. The upper tendon of the rotator cuff is often affected.
Calcific tendonitis
In calcific tendonitis, calcium deposits form in the tendons of the shoulder. These deposits can cause pain and restricted movement.
Frozen shoulder
Frozen shoulder is an inflammatory disease of the synovial membrane and joint capsule in which the shoulder gradually stiffens and movement is severely restricted. The exact cause is often unknown and the condition can lead to chronic shoulder pain.
Bursitis
Bursae are fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction in the joints. Inflammation of these bursae can lead to pain and swelling in the affected shoulder.
Shoulder osteoarthritis
Similar to other joints, osteoarthritis can also occur in the shoulder. The cartilage in the shoulder wears away, leading to chronic joint pain and restricted movement.
Shoulder dislocation
A shoulder dislocation is a dislocation of the shoulder joint in which the upper arm bone protrudes from the socket. This causes severe pain and usually requires immediate medical treatment.
Herniated disc
A herniated disc in the cervical spine occurs when a piece of disc pushes into the spinal canal. This can affect nerves in the shoulder and lead to severe pain and numbness.
Tendon rupture
Tendon rupture refers to partial or complete destruction of a shoulder tendon (biceps tendon). This can lead to significant pain, loss of strength and limited function and often requires surgical treatment.

Treatment of shoulder pain
In order to determine the right treatment for your shoulder pain, you need to see a doctor for a diagnosis. A physical examination and imaging techniques such as an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) will be used to determine the cause of your pain.
Fortunately, many types of shoulder pain can be treated with conservative therapies in the early stages. However, if you miss the right time frame or you have suffered a serious injury, surgery may be the only treatment option.
Below we have listed possible treatments for shoulder pain:
- Physiotherapy and exercise
In most cases, treatment by a physiotherapist is recommended for shoulder injuries or illnesses. Therapeutic exercise helps to relieve pain and maintain or regain mobility. - Immobilization
Depending on the diagnosis, temporary immobilization of the affected shoulder is advisable. This applies to shoulder dislocation, for example. It is advisable to immobilize the shoulder for the first three weeks after the injury. However, depending on the cause of the pain, immobilizing the shoulder can also be counterproductive - it is therefore important to obtain a medical diagnosis in order to react appropriately. - Treatment with painkillers
Medication such as ibuprofen or cortisone have an anti-inflammatory and therefore pain-relieving effect in acute shoulder pain. However, it should be noted that these preparations should not be taken for longer than prescribed by the doctor. - Surgery
Surgery can be an effective option for shoulder pain if it is caused by injuries such as fractures or torn ligaments. In such cases, a specialist can repair the structural damage. This can relieve the pain and restore normal shoulder function. After surgery, careful aftercare and rehabilitation is important to aid recovery. - Arthroscopy
An arthroscopy is a minimally invasive technique that can be used to diagnose and treat shoulder pain due to a variety of causes. In this procedure, the surgeon inserts tiny instruments through small incisions in the shoulder to identify or treat the cause of the pain.

Relieving shoulder problems with movement
Many sufferers intuitively adopt a protective posture when in pain or immobilize the shoulder joint permanently. While this is natural for acute pain and, depending on the cause, also is advisable, exercise is extremely important in the long term to relieve chronic pain in the shoulder region and maintain or regain mobility.
There are various exercises that can be used to alleviate shoulder problems. Neck stretches, for example, can help to release tension in the muscles and improve posture. Circling the shoulders also helps to relax the shoulder area and make the joint more mobile. If you want to extend the range of movement even further, you can help by stretching your arms.
After an injury or illness, it can be very challenging to get back on track with exercise. You may be wondering which exercises are best in your case or how often you should repeat them. You may also be concerned about whether you are doing the exercises correctly or whether you are harming yourself by not doing them right.
This is where Akina comes in. Our AI-supported software acts as your personal trainer at home and supports you with immediate feedback during therapeutic training for musculoskeletal pain. With Akina Cloud, you can connect with the physiotherapist of your choice to get the most out of the combination of personal and digital care. Sounds interesting? Find out more about our mission and product in the article Akina - Better begins today or sign up to the Akina newsletter to be notified when we launch. We look forward to welcoming you!





